How do search engines work and why is it important for business?

Search engines are the internet window for businesses. They gather colossal amounts of information on each website, break it down, and decide how well it responds to a particular request. But with so much data, how do search engines actually work?
To more efficiently search, classify, and rank the billions of pages that make up the web, search engines use sophisticated algorithms that make decisions about the quality and relevance of an article or video.
This is a complex process that involves the processing of significant amounts of data, and all of them must be presented in the most convenient way for the end user.
Search engines analyze all of this through numerous different ranking factors based on a user’s query. This is the relevance of the question entered by the user, the quality of the content, speed, metadata and much more.
Each data point is combined to help the search engine calculate the overall “quality” of the page. The site is then ranked based on these calculations and is made available to the user below or above on the search engine results page (SERP).
Knowing the hidden behind-the-scenes processes that occur in search engines to make these decisions helps businesses understand why certain pieces of content rank highly, but it also helps create new content with potentially higher rankings.
Let’s take a look at the general procedures on which each search engine algorithm is built, and then analyze the mechanisms of their work on the example of giants Google and Youtube.
How Search Engines Work
To be effective, search engines must accurately interpret the information available and present it to users logically. To do this, the systems perform three main actions - these are scanning, indexing and ranking.
Through these actions, they discover recently published content, store the information on their servers, and organize it for our consumption. Let’s take a look at what happens during each of these actions:
- Scanning. Search engines send web crawlers, known as bots or spiders, to view a site’s content. Paying close attention to new websites and recently changed content, crawlers analyze URLs, sitemaps, and code to determine the type of content being displayed.
- Indexing. After scanning the site, the systems must decide how to organize the information. The indexing process is that they check the website data for positive and negative ranking signals and store them in the appropriate place on their servers.
- Ranking. During the indexing process, search engines begin to make decisions about where to display specific content on a search results page. Ranking is done by evaluating a number of factors based on user query preferences, quality, and relevance.
During this process, computers must determine the value that any website can potentially provide to the end user. These decisions are guided by an algorithm. Understanding how a search algorithm works helps create effective content that ranks higher for each platform.
Whether it’s RankBrain for Google and YouTube, the Graph and Spatial Section Tree (SPTAG) for Bing, or the proprietary codebase for DuckDuckGo, each platform uses a unique series of ranking factors.
If a business takes these factors into account when creating content for a website, adapting certain pages for good rankings will become easier.

Google and Youtube search engine algorithms
Each search engine processes search results in its own way. We’ll take a look at the two most popular platforms in today’s market (including a video platform) and look at how they make decisions about the quality and relevance of content.
How Google’s search engine works
Google is the most popular search engine on the planet. It occupies more than 90% of the market, receiving more than 3.5 billion individual search queries daily. It is known that Google’s search algorithms quite cleverly determine the priorities of websites and sometimes cause distrust and critical attitude of users.
New sites are created every day. Google can find these pages by clicking on links from existing content they’ve crawled previously, or when the website owner submits their sitemap directly.
Any updates to existing content can also be sent to Google if asked to review a specific URL. This is done through Google Search Console.
While Google doesn’t say how often sites are viewed, eventually any updated content related to existing content is bound to be found.
When bots collect enough information, they return it to Google for indexing.
Indexing begins with the analysis of the site’s data, including text content, images, videos, and the technical structure of the site. Google looks for positive and negative ranking signals, such as keywords and site freshness, to understand the quality of the page being crawled and its importance to the user.
The Google Sites Index contains billions of pages and 100,000,000 gigabytes of data.
To organize this information, Google uses a machine learning algorithm called RankBrain and a Knowledge Graph knowledge base. They work together to help the system deliver the most relevant content to the user. Once the indexing of the site is completed, Google moves on to ranking.
Everything up to this point happens invisibly to humans, in the background, before the user interacts with Google’s search features.
Ranking occurs depending on what the user is looking for.
In doing so, Google looks at five main factors:
- The value of the query. What is the end user’s goal? Google uses queries to determine a person’s intent (for example, to buy a car or see its characteristics). It analyzes each query using complex language models based on people’s past searches and behavior.
- The relevance of the web page. Once Google has determined the purpose of a user’s search query, it looks at the content of the web pages with the ranking to determine which one is the most relevant. The main factor is keyword analysis. Keywords on a website should match Google’s understanding of the question asked by the user.
- Quality of content. By selecting keywords, Google takes it a step further and checks the quality of the content on the right pages. This helps to prioritize more accurately by looking at the authority of a given site, as well as page rank and freshness.
- Usability of pages. Google prefers sites that are easy to use. Usability encompasses everything from speed to responsiveness.
- Additional context and settings. This step configures search by past user experience and specific settings on the Google platform.
As soon as all this information is qualitatively processed, google’s algorithm will provide search results on the monitor screen that look something like this:
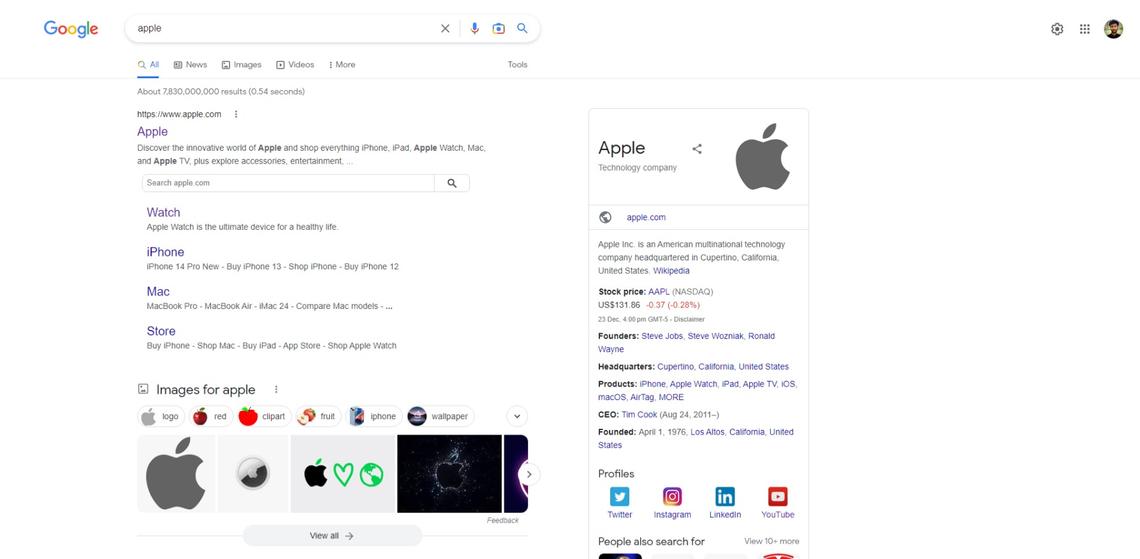
Let’s break down the search results page:
- A custom request. A question asked by a Google user.
- Purchases on Google. The system considers the purpose of the request as the search for goods to buy. As a result, products that match this purpose are extracted from the index and displayed first in the results.
- Featured snippet. Google presents specific information from the SERPs so that the user can view more easily without leaving the search results page.
- Results with the highest rating. The first site listed in the results is the site that Google thinks best fits the purpose of the user’s query. The best result is chosen based on the five ranking factors we discussed earlier.
- People are also looking. this field is the result of the Knowledge Graph. It gives users a quick way to move on to another search that can better match their intent.
Such a detailed provision of information became possible only because the system disassembled into fragments and stored billions of pages in memory. Before the user performs the search, Google checked the sites to find out which keywords and intents they best matched.
This process allows you to fill in the results pages within a fraction of a second when performing a search and helps Google give us the most relevant content.
As the most popular search engine in the world, Google has more or less managed to create the basis for how the rest of today’s search engines look at content.
Most marketers specifically tailor their content to rank on Google. On the one hand, it is the correct use of forces and budgets. On the other hand, they potentially miss opportunities to promote content on other platforms.
YouTube Search Algorithm
The YouTube platform is the most popular video hosting service. Their search engine operates effectively under rules similar to those of Google, which owns the platform, and it focuses on keywords and relevancy.
The algorithm is broken down into two separate functions – ranking videos and finding relevant recommendations. Below we will analyze them in more detail.
The specific reasons why some videos stand above others, like everything inside Google, are hidden from prying eyes. However, most experts are inclined to the novelty of the video and the frequency of downloading the channel as the most important factors.
In terms of recommendations, a recent research paper detailed YouTube’s top priorities, such as scale, freshness, and noise:
- Scale. 300 hours of video is uploaded to YouTube every minute, and the platform already has about 1.3 billion users. This greatly complicates the analysis of information, so now the main task of the algorithm is to sift through a huge amount of data for each user.
- Freshness. YouTube tries to balance its choice based on how long ago the video has been uploaded, as well as user behavior in the past.
- Noise. Due to the different content that most users look at on YT, it is difficult for artificial intelligence at any time to analyze what is most relevant – the analysis of “noise” helps to weed out the unnecessary.
These and possibly other ranking factors lead to the formation of recommendation pages for each individual user account. As a result, we enjoy those videos that we are really interested in.
This shows how “Subscriptions” affect the provision of YouTube search results. When a user subscribes to a particular channel, it increases their ranking in search results, recommendations, and choosing what to watch next.
Other ranking factors include what the user is watching, how long they’ve been passionate about different videos, and what the overall popularity of The Videos is on YouTube.
Let’s analyze the search results using an example:
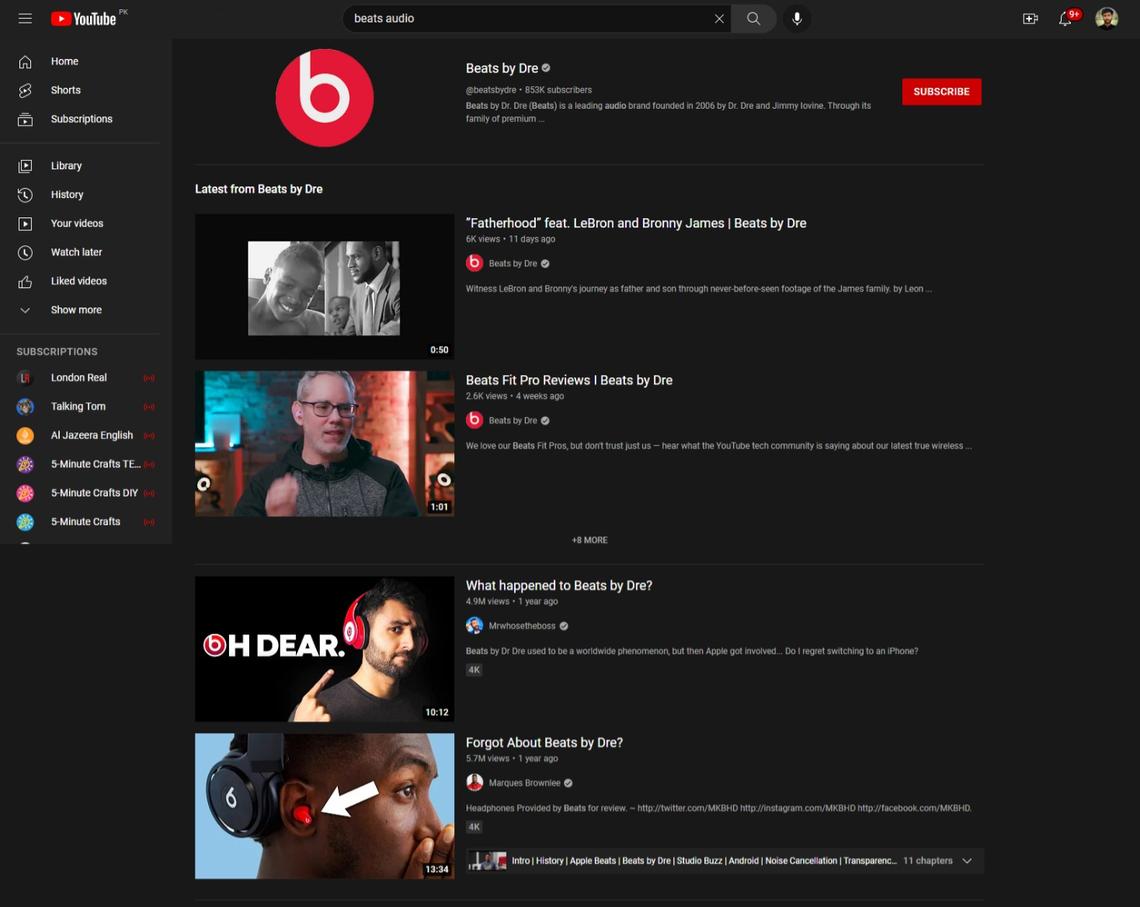
The best result is the most viewed video. This is followed by a newer download with fewer views but with an exact keyword match. The third video has more views than the second, but without an exact keyword match – it’s also a slightly older download.
Based on these results, we see that popularity breeds popularity and is one of the most important youTube ranking factors – and even higher than the novelty of a video with an exact keyword match.
To get good rankings on YouTube, you’ll need an authoritative profile and a consistent download pace. Their focus on the popularity and strength of the profile requires more investment in marketing – these investments quickly pay off for brands that concentrate their efforts on the video platform.
Conclusion
Understanding how search engines work helps create better content.
When you know how certain platforms display their results, it’s easier to create content with ranking potential. This insight also helps you diagnose why other types of content rank better or worse than your own.
Based on this, we’ve put together five tips to help you create better content:
- Understanding user intent. Each search engine prefers the content that is most relevant to the user’s search query.
- Relevant keywords. Incorporating relevant keywords into your content will help search engines find and index pages more easily.
- Knowledge of the target audience. Keyword matching will require a deep understanding of customers and how they think about your product and your market.
- New content helps improve rankings. Posting new content or updating existing content helps increase a site’s ranking and brand authority.
- Getting authoritative links. The more people link to a page, the better it will look to search engines. This will speak of its high value to users and the relevance of the content.
At the end of the day, it all comes down to understanding the customer. You can’t create content that ranks well if you don’t know what your target audience needs.
Tags
Share
About Me
Join our newsletter
Get business tips once a month
Legal Stuff
